The spatial organization of genes and other genetic elements within the 3-D
space of the nucleus is important for regulating gene expression. Understanding how this
spatial organization is established and maintained throughout the life of a cell is key
to elucidating the many layers of gene regulation. Quantitative methods for studying
nuclear organization will lead to insights into the molecular mechanisms that maintain
 gene organization as well as serve as diagnostic tools for pathologies caused by loss of
nuclear structure. However, biologists currently lack automated and high-throughput methods
for quantitative and qualitative global analysis of 3-D gene organization.
gene organization as well as serve as diagnostic tools for pathologies caused by loss of
nuclear structure. However, biologists currently lack automated and high-throughput methods
for quantitative and qualitative global analysis of 3-D gene organization.
Confocal microscopy and fluorescence in-situ hybridization (FISH) is used as a
cytogenetic technique to localize the presence of specific DNA sequences in 3-D space.
FISH uses probes that bind to specific targeted locations on the chromosomes, appearing as
fluorescent spots in 3D images obtained using fluorescence microscopy. Manual counting of
spots in FISH images is tedious, as the number of nuclei and spots can be large, and spots
will span across multiple images, also presenting serious constraints on the acquisition of
large data sets required for robust statistical analyses.
Moreover, manual analysis is
user-dependent in a clinical setting, as the task can be subjective and specific training is
often lacking.
In order to do accurate spot counting in 3-D it is required to detect and localize the presence
of these spots within the data sets obtained from confocal misroscopy and then segment their
boundaries and classify them from other biological structures and debris present within
the data sets. We have built an automated system capable of detection, segmentation and
classification of these 3-D spots and also capable of doing robust statistical analysis on these
segmented regions such as volumetric analysis, calculation of density of a spot cluster,
compartmentalization of these spots and their position with respect to the nucleus boundary in a
radial manner.
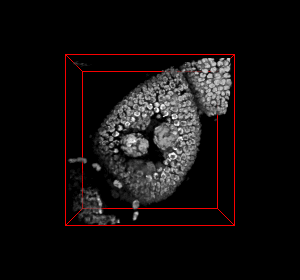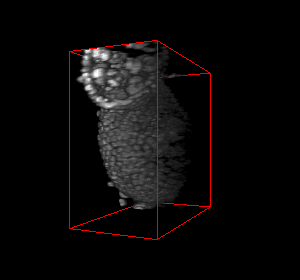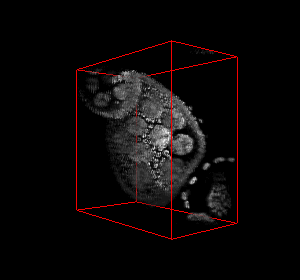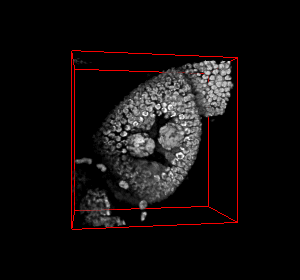
The video seq.1 shown at the top right shows the channel area within a single nucleus and the spots
present within them. The video at the top right also shows the detection and segmentation output of our
method. The video seq.2 shown at bottom left is the 3-D projection of the segmented spots rotating
around the x-axis.
This work was a collaborative effort with Prof. Giovanni Bosco in the
Dept. of Molecular and Cellular Biology, College of Science,
University of Arizona.
Publications:
-
Sundaresh Ram and Jeffrey J. Rodriguez, "Symmetry-Based Detection of Nuclei in Microscopy Images," in Proc. IEEE Intl. Conf. on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Vancouver, Canada, May 26-31, 2013, pp. 1128-32. [ PDF ]
- Sundaresh Ram, Jeffrey J. Rodriguez and Giovanni Bosco, "Size-Invariant Cell Nucleus Segmentation in 3-D Microscopy," 2012 IEEE Southwest Symp. on Image Analysis and Interpretation, April 22-24, 2012, Santa Fe, NM, pp. 37-40. [ PDF ]
