Antoine's Equation
Antoine's equation is a relatively simple empirical equation that correlates vapor pressure and temperature data extremely well. The Antoine Equation usually stays in the same form, but may change units depending on the source. For the version found in "Elementary principles of Chemical Engineering" by Felder and Rousseau, the units for Pressure are mmHg, and Temperature in degrees Celsius. Another resource which provides Antoine's Equation information is the NIST Webbook website. At NIST, the units for Pressure are usually bar, and Temperature is usually in Kelvin. Regardless of the units, the Antoine's equation is dependant on the specific compound of interest, and as a result gives constants A, B, and C.
Here are two possible forms of the Antoine's equation:
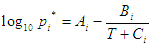 |
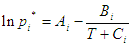 |
If given Acetone and the constants A=7.11714, B=1210.595, and C=229.664, find the vapor pressure at T=25oC using the log base ten version of Antoine's Equation.
© 2003 Arizona Board of Regents for The University of Arizona
